Non-maximum suppression
Description
Non-maximum suppression (NMS) is a post-processing step in many computer vision applications. In the context of object detection, it is used to discard redundant detections and to achieve a single bounding-box for each detected object. After applying the object detection method, the output looks like: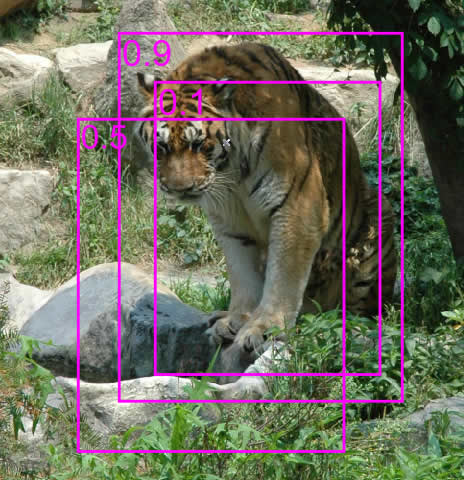

Method
0. Sort all objects by score in descending order.1. Compute area for every object.
2. Discard objects with score <= 0.6 (0.6 value as example)
3. Compute the intersection between 2 objects. A dominant object must have a highest score.
4. Compute the IOU or Jaccard index.
5. Discard non dominant object with IOU >= 0.5 (0.5 value as example).
EXAMPLE
/* ANSI C89, C99, C11 compliance */
/* The following example shows the usage of non-maximum suppression. */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#define MIN(a,b) (((a)<(b))?(a):(b))
#define MAX(a,b) (((a)>(b))?(a):(b))
#define DISCARD_BOXES_SCORE 0.6 /* boxes with score <= 0.6 to discard */
#define DISCARD_BOXES_IOU 0.5 /* boxes with IOU >= 0.5 to discard */
/*
a---
| |
---b
*/
struct OBJ_DET {
unsigned int n_class; /* class of object */
float r_score; /* detection score */
unsigned int n_x_a; /* bounding box upper left corner x coordinate */
unsigned int n_y_a; /* bounding box upper left corner y coordinate */
unsigned int n_x_b; /* bounding box bottom right corner x coordinate */
unsigned int n_y_b; /* bounding box bottom right corner y coordinate */
unsigned int n_width; /* bounding box width */
unsigned int n_height; /* bounding box height */
unsigned int n_area; /* bounding box area */
unsigned int n_state; /* state of detection: 0 - non active, 1 - active */
};
/* insertion sort in descending order */
void insertion_sort_do(struct OBJ_DET *p_st, size_t n_size) {
size_t i, j;
struct OBJ_DET st_val;
for (i = 1; i < n_size; i++) {
memcpy(&st_val, &p_st[i], sizeof(struct OBJ_DET));
for (j = i; j > 0 && st_val.r_score > p_st[j - 1].r_score; j--) {
memcpy(&p_st[j], &p_st[j - 1], sizeof(struct OBJ_DET));
}
memcpy(&p_st[j], &st_val, sizeof(struct OBJ_DET));
}
}
/* The Jaccard index, also known as Intersection over Union (IoU) and the Jaccard similarity coefficient. */
float intersection_over_union(unsigned int n_area_inter, unsigned int n_area_a, unsigned int n_area_b) {
return (float)n_area_inter / (float)(n_area_a + n_area_b - n_area_inter);
}
int main() {
struct OBJ_DET st_ds[3] = {{0, 0.7f, 1, 1, 0, 0, 4, 4, 0, 1}, {0, 0.2f, 2, 2, 0, 0, 4, 4, 0, 1}, {0, 0.8f, 1, 1, 0, 0, 4, 4, 0, 1}};
size_t i, j, n_size;
int z_xx_a, z_yy_a, z_xx_b, z_yy_b, z_w, z_h;
float r_iou;
n_size = 3; /* number of objects */
insertion_sort_do(&st_ds[0], n_size); /* sort detections in descending order */
for (i = 0; i < n_size; i++) { /* calculate area */
st_ds[i].n_area = st_ds[i].n_width * st_ds[i].n_height;
st_ds[i].n_x_b = st_ds[i].n_x_a + st_ds[i].n_width;
st_ds[i].n_y_b = st_ds[i].n_y_a + st_ds[i].n_height;
if (st_ds[i].r_score <= DISCARD_BOXES_SCORE) /* discard object */
st_ds[i].n_state = 0;
}
for (i = 0; i < n_size; i++) {
if (st_ds[i].n_state != 0) {
for (j = 0; j < n_size; j++) {
if ((i != j) && (st_ds[j].n_state != 0) && (st_ds[i].n_class == st_ds[j].n_class)) {
z_xx_a = MAX(st_ds[i].n_x_a, st_ds[j].n_x_a);
z_yy_a = MAX(st_ds[i].n_y_a, st_ds[j].n_y_a);
z_xx_b = MIN(st_ds[i].n_x_b, st_ds[j].n_x_b);
z_yy_b = MIN(st_ds[i].n_y_b, st_ds[j].n_y_b);
z_w = z_xx_b - z_xx_a;
z_h = z_yy_b - z_yy_a;
if ((z_w > 0) && (z_h > 0)) {
r_iou = intersection_over_union(z_w * z_h, st_ds[i].n_area, st_ds[j].n_area);
if (r_iou >= DISCARD_BOXES_IOU)
st_ds[j].n_state = 0; /* discard object */
}
}
}
}
}
for (i = 0; i < n_size; i++) {
if (st_ds[i].n_state != 0)
printf("Object %lu is active\n", i);
}
return 0;
}
REFERENCES: