Leaky rectified linear unit (Leaky ReLU)
Description
In the context of artificial neural networks, the Leaky ReLU is an activation function defined as: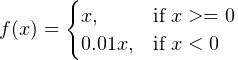
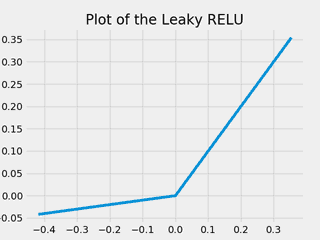
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
def lrelu_forward(x):
return np.where(x > 0, x, x * 0.1)
x = np.random.rand(10) - 0.5
x = np.append(x, 0.0)
x = np.sort(x)
y = lrelu_forward(x)
plt.style.use('fivethirtyeight')
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot(x, y)
ax.set_title("Plot of the Leaky RELU")
plt.show()
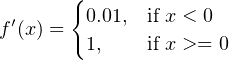
tf.nn.leaky_relu(
features,
alpha=0.2,
name=None
)
Pytorch form of Leaky ReLU:
classtorch.nn.LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.01, inplace=False)
Forward propagation EXAMPLE
/* ANSI C89, C99, C11 compliance */
/* The following example shows the usage of Leaky RELU forward propagation. */
#include <stdio.h>
float lrelu_forward(float x){
return (x>0) ? x : 0.01f * x;
}
int main() {
float r_x, r_y;
r_x = 0.1f;
r_y = lrelu_forward(r_x);
printf("Leaky RELU forward propagation for value x: %f\n", r_y);
return 0;
}
Backward propagation EXAMPLE
/* ANSI C89, C99, C11 compliance */
/* The following example shows the usage of Leaky RELU backward propagation. */
#include <stdio.h>
float lrelu_backward(float x){
return (x > 0) ? 1.0f : 0.01f;
}
int main() {
float r_x, r_y;
r_x = 0.1f;
r_y = lrelu_backward(r_x);
printf("Leaky RELU backward propagation for value x: %f\n", r_y);
return 0;
}
REFERENCES: